简介
DCGAN即使用卷积网络的对抗网络,其原理和GAN一样,只是把CNN的卷积技术用于GAN模式的网络里,G(生成器)网在生成数据时,使用反卷积的重构技术来重构原始图片。D(判别器)网用卷积技术来识别图片特征,进而作出判别。
https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434
架构

判别器
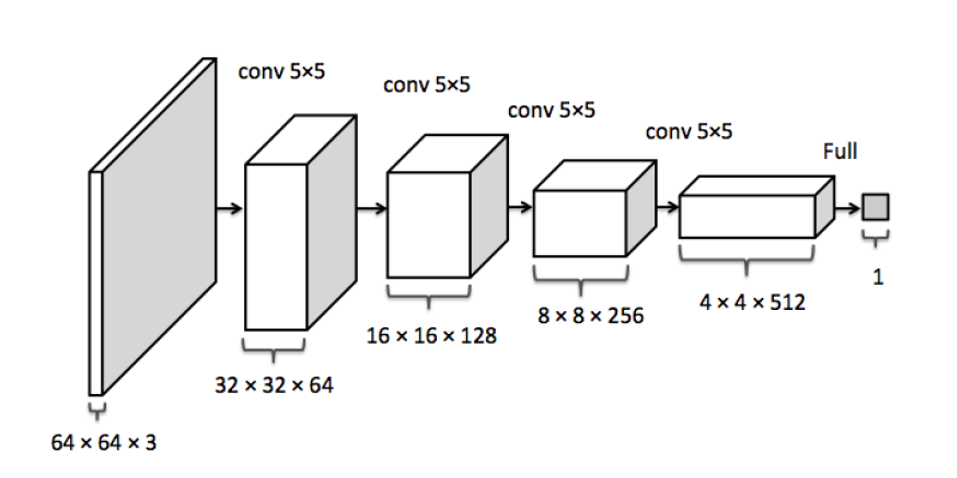
生成器
在DCGAN中,生成式模型G(z)使用一个比较特殊的深度卷积网络来实现,如下图所示:
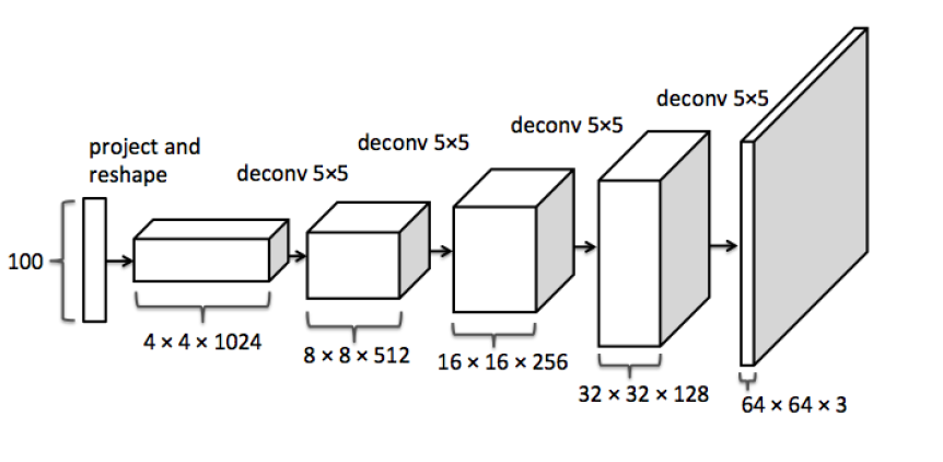
反卷积
从前面两幅图中可以看出,DCGAN的生成式模型G(z)中出现了上采样(upsampling)。
卷积神经网络的下采样很好理解,加入pooling层即可,然而这里的上采样要如何实现呢?
这里,DCGAN通过“微步幅卷积”(fractionally-strided convolution)进行上采样。
假设有一个3×3的输入,希望输出的尺寸比这要大,那么可以把这个3×3的输入通过在像素之间插入0的方式来进行扩展,如下图所示。当扩展到7×7的尺寸后,再进行卷积,就可以得到尺寸比原来大的输出。
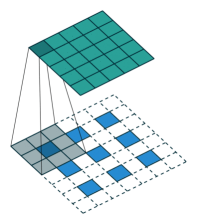
特点

调优

https://github.com/hindupuravinash/the-gan-
实现
深度卷积神经网络生成Mnist手写数据集—-DCGAN
导入环境
import numpy as np |
数据准备与超参数设置
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('data') |
数据处理
def get_inputs(noise_dim, image_height, image_width, image_depth): |
构建DCGAN网络结构
生成器
def get_generator(noise_img, output_dim, is_train=True, alpha=0.01): |
判别器
def get_discriminator(inputs_img, reuse=False, alpha=0.01): |
计算损失值
def get_loss(inputs_real, inputs_noise, image_depth, smooth=0.1): |
初始化优化器
def get_optimizer(g_loss, d_loss, learning_rate=0.001): |
显示图片
def plot_images(samples): |
开始训练
def train(noise_size, data_shape, batch_size, n_samples): |